Introduction
Diseases of the joints are better known as rheumatic diseases. Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and gout are common varieties of arthritis encountered in clinical practice. Rheumatism is a broad term used for injury or inflammation of soft tissues. To understand the disease process in various types of arthritis, it is necessary to understand the basic make up of a joint.
Diagram of a Typical Joint is Shown Below:
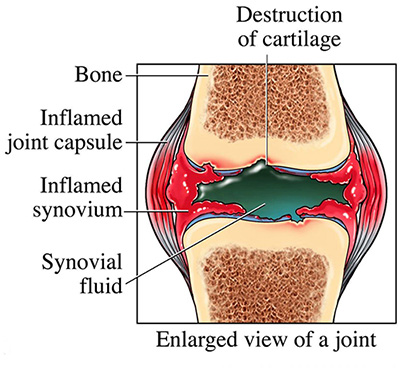
Pain, inflammation (swelling), fever, loss of function, and morning stiffness are cardinal features of arthritis. Based on the character of pain, involvement of the joint and laboratory tests, the final diagnosis is arrived at. Some form of arthritis involves other organs like heart and muscles. It is common in rheumatic and rheumatoid arthritis, respectively.
Cause
Ama (substance produced by improper functioning of the digestive system) is considered to be root cause of Ama-vata (Rheumatoid arthritis) in Ayurveda. It circulates in the blood and finally collects in the joint surface causing pain and loss of function. Rheumatoid arthritis accounts for 15 per cent of the total rheumatic disorders. The incidence is more common in women. The disease is more prevalent in cold and damp conditions.
Pathology of Amavata in Ayurveda
Arthritic diseases have been known to exist since antiquity. Probably the earliest description of arthritis occurs in Athravaveda, around 1000 B.C.1 Charaka Samhita, written in the post Vedic period, has dealt more accurately with the etiology, Ayurveda suggests that arthritis is caused primarily by an excess of ama (byproduct of improper digestion) and lack of agni (digestive fire). This can be caused by poor digestion and a weakened colon, resulting in the accumulation of undigested food and the buildup of waste matter. Poor digestion allows toxins to accumulate in the body, and problems with the colon allow the toxins to reach the joint symptomatology, diagnosis and management of arthritis. Prognosis of arthritis, as proclaimed by the ancient physicians of India, remains unaltered.
Signs and Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic form of arthritis characterized by pain and inflammation of more than two joints. It commonly strikes small joints of the hands. The arthritis has symmetrical pattern unlike gout and osteoarthritis. The finger joints are worst effected by rheumatoid arthritis. Deviation of hand and z- shaped deformity of the thumb are special features of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid factor is found to be positive in 80 per cent of the patients. Erythrocytic sedimentation rate (ESR) is on the higher side in acute cases. Total leukocyte count (TLC) and differential leukocyte count (DLC) are also high. In rare cases anemia is found. Rheumatoid arthritis not only affects joints but it attacks organs like heart, muscle and eye also.
Precautions and Diet
The patient should consume fresh vegetables, garlic and black pepper. Exposure to cold and damp conditions should be avoided. Use of curd is prohibited at night. White grams, pea, soybean, potato, and cold water bath should be avoided.
Wheat, ghee, sathi variety of rice, ginger, garlic, punarnava, pomegranate, mango, and grape are useful in rheumatoid arthritis.
