Introduction
In Ayurveda, snayu refers to the ligaments and kandra stands for tendons. The anatomical study of the ligaments is known as desmology. Joint represents the articular apparatus, whereas, muscle, ligament, and tendon constitute the extra-articular apparatus. Diseases of the joints are better known as rheumatic diseases. Sandhigatavata (osteoarthritis), amavata (rheumatoid-arthritis) and vata-rakta (gout) are common forms of arthritis seen in clinical practice. Rheumatism is a broad- term used for inflammation or injury of the soft tissues. Cervical spondylosis, lumbar- spondylosis and sciatica or sciatic neuritis are other significant diseases included in this segment.
Anatomy of the joint
To understand the pathogenesis of diseases of andhi (joints), sanyu (ligaments), asthi (bones) and kandara (tendons), it is necessary to understand the anatomy of the joint.
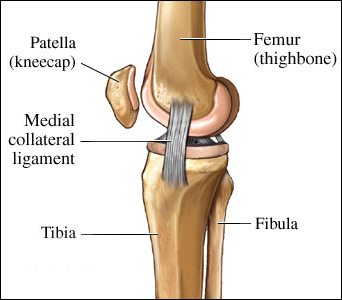
The joint has a synovial membrane which covers the joint from inside and the cartilage, normally, covers the articulating junction of the bones. The cartilage merges at its free edges with the internal synovial membrane lining of the joint cavity, containing a small amount of fluid known as the synovial fluid. The cartilage obtains nutrients from the synovial fluid. Synovial fluid plays the role of the shock absorber as it prevents friction between the bones.
Ligament versus tendon
A tendon is a fibrous connective tissue, helping in the attachment of the muscle to bone. Further, tendons also help attach the muscles to structures for example, the eyeball. A tendon helps in the movement of the bone. A ligament is a connective tissue which helps in attachment of one bone with another, and helps in holding the structures together and keep them stable.
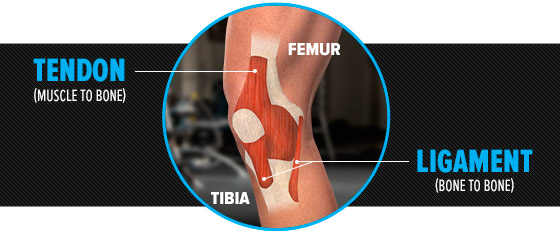
Significance of ligament and tendon at clinical level
Snayu (ligaments) are the basically structures present in the human body and have a proximate relationship with the biological air or the functional element… vata. Snayu are classified according to the anatomy, function and specific location. Injury or trauma to snayu is very painful and the pain is because pain is the attributed to the biological air or the functional element… vata.
The concept of Snayu Marma, which are best defined as vital points also explains the importance of snayu which are to be protected at any cost. Clinical manifestations like grudrasi (sciatica) and pakshaghata (paralysis) occur due to the impairment in functional role of snayu along with shira (blood vessels) and Kandara (tendon). In the present era, the incidence of extra-articular diseases like tendinitis, fibrositis, injury to the ligaments, and non-articular-rheumatism, are increasing at a rapid rate.
Types of ligament as per Ayurveda
Snayu has been described as Vaatavahini Nadi… structures carrying the biological air…vata). In Ayurveda, four types of snayu have been described.
- Pratanavathi Snayu (Branched): Pratanavathi snayu are present in all the joints and the extremities.
- Vrutha Snayu (Circular): Vrutha snayu are circular in shape and are known as Kandara in Ayurvedic anatomy.
- Sushira Snayu (Porous): Sushira snayu are porous in nature and are found in the end of stomach and intestines and urinary bladder.
- Pruthu Snayu (Flat): Pruthu snayu are flat in nature and are found in the chest, sides, head and back.
Based on their distribution in the Shadanga (six body parts of human body), snayu are nine-hundred in counting. Among these, six-hundred are present in the extremities, two hundred and thirty in found. Seventy is found, urdhavajatrugata (above towards the neck). Snayu helps the joints in bearing heavy weight. The injury to bones, muscles, blood-vessels, and joints may not be as critical as the ligaments.
Myasthenia Gravis
As regard pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis is concerned, it is similar to diseases like rheumatoid-arthritis, sanayugata-vata (biological air present in flesh and ligament), sanayu-mamsagata-vata (biological air is present in flesh and ligament), kapha-avrita-vyana-vayu (the biological water being layered with vyana vata…special form of biological air) and the names of diseases with presentation of similar clinical findings like khanja (limping), urustambha (thigh-fatigue).
Sanayugata-vata or Vatavrit sanayu roga (Fibromyalgia Syndrome)
Vatavrit sanayu roga or sanayugata-vata (fibromyaligia), is a characterised by musculoskeletal pain and fatigue of wide-spread nature, which strikes in five percent of the total population. The exact reason behind fibromyaligia is largely, unknown. Fibromyaligia is characterized by widespread pain in the muscles, tendons and ligaments of the fibrous tissues in the human-body.
Conclusion
Snayu (ligaments) present in the human body are closely allied to the biological air…vata. Snayu is one of the extra-articular or subsidiary tissue, which plays an important role in the posture of the human-body. Snayumarma, which are better known as vital points in Ayurvedic anatomy are specific locations in the human body which are characterized by the predominance of the ligament. The study of human-anatomy is very much vital for preventive and curative aspect. Knowledge of snayu (ligaments) is very important for physicians as well as surgeons who are dealing with surgical removal of foreign bodies.
